How To Properly Exfoliate Your Skin
Posted by Globex Beauty Solutions on 14th Sep 2021
What's the difference between peels and scrubs? We often speak of ‘scrubs’ to refer to a product with mechanical actions that make it possible to exfoliate the skin through friction, and ‘peels’ to refer to a product that offers a chemical action in which specific compounds separate dead cells and eliminate them.
SCRUBS
Scrubbing is a mechanical exfoliation process – it is the best known and most frequently applied process. It consists in applying a product (gel or cream) containing natural grains (e.g. fruit seeds or polyethylene granules) which, through massage, make it possible to eliminate dead cells and unclog the pores.
This scrub is carried out through circular motions applied to the face, avoiding the eye area and adapting the scrub pressure to the needs of the specific skin area.
We can also find scrubs made from soft clays that dry on the skin. It is through the circular movements used to remove the product that dead cells are exfoliated.
It provides a deep epidermal cleansing, perfect for purifying and remedying small imperfections like blackheads, and brightening a dull skin complexion.
Thanks to the massage, it stimulates microcirculation and cell regeneration. As a result, the skin becomes smoother and more radiant.
PEELS
Unlike scrubs, where exfoliation is carried out through a mechanical action, peels simply need to be applied and left on the skin for a few minutes.
Peels are based on fruit acids (AHA or Alpha Hydroxy Acids) such as glycolic or lactic acid, for example, and provoke chemical exfoliation.
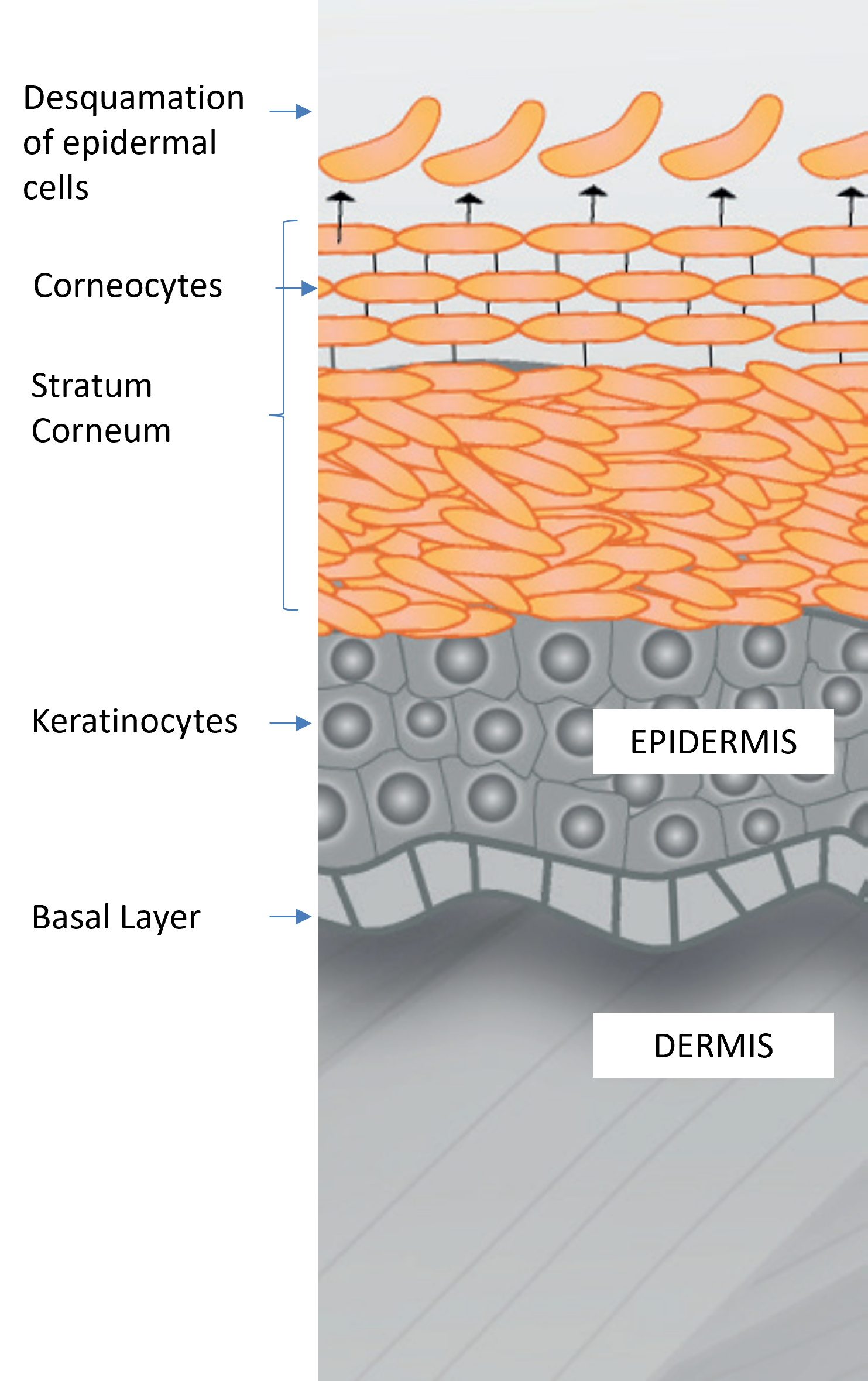
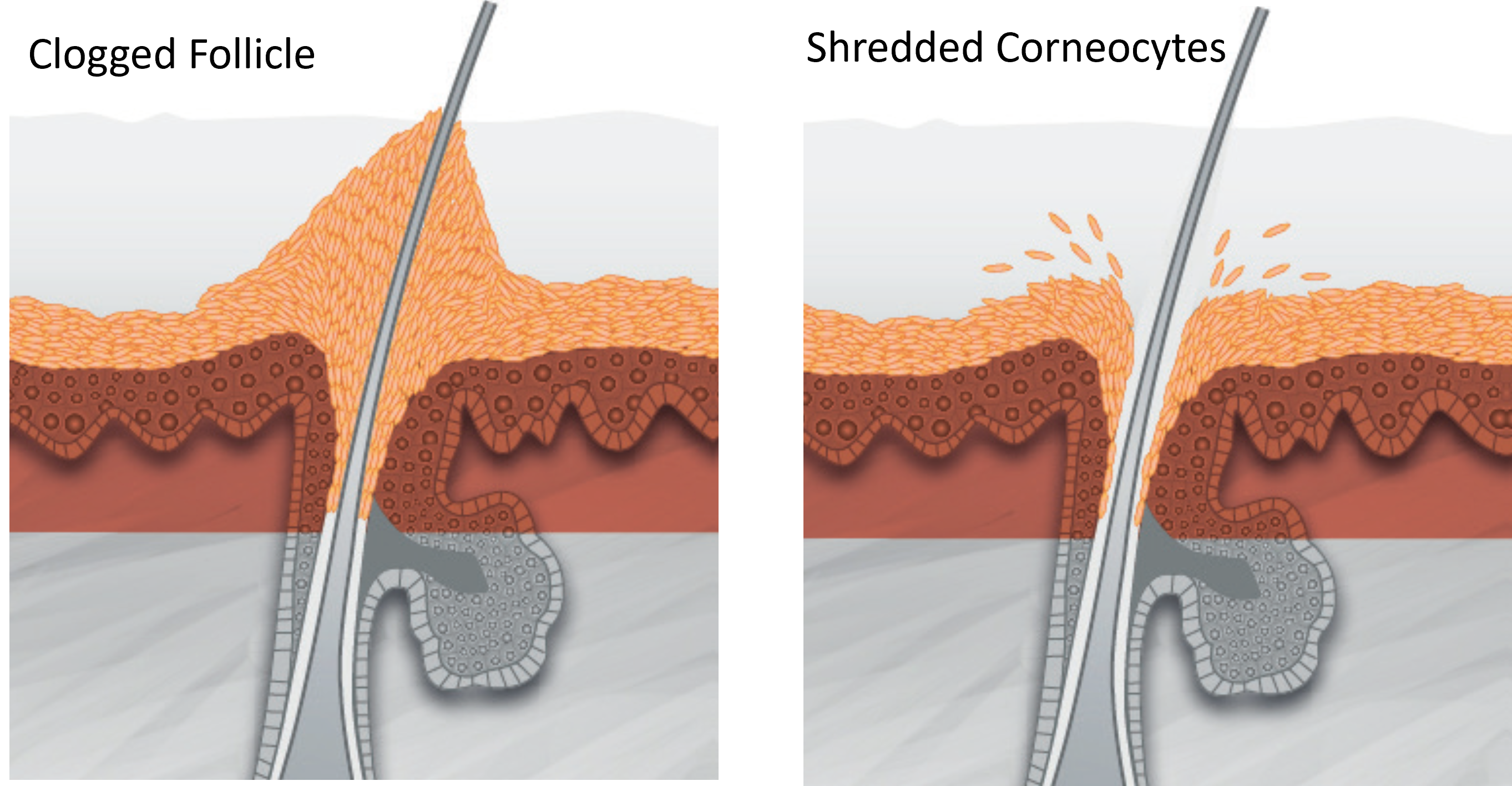
If the stratum corneum is clogged with dead cells, its protective role is weakened
This exfoliating effect due to mechanical or chemical action is followed by an acceleration of cell renewal and a stimulation of the collagen and elastin synthesis, consequently offering tone and elasticity.
It increases synthesis of the glycosaminoglycans (which have a great affinity for water) and, as a result, the water-retention capacity of the dermis, which also promotes suppleness within the skin.
ENZYMATIC EXFOLIATION
This forms part of chemical exfoliation. The only difference is that the exfoliating agents are enzymes or proteases from fruits (papain from papaya, bromelain from pineapple, ficin from fig, etc.). These biological activators are very important for the majority of the body’s biochemical reactions.
This is because they multiply reaction speeds of ingredients by anything from 1,000 to several billion: without these activators, the biochemical reactions of these ingredients could not take place.
Enzymes dissolve the proteins of dead cells in order to eliminate these, by separating them from the surface layer of the epidermis.
Enzymatic exfoliators have the ability to weaken the chemical bonds between corneocytes, and to ‘digest’ keratin proteins.
Proteases’ action is an essential factor of desquamation, closely associated with the process of proliferating
basal cells within the germinal layer. This exfoliation causes no irritation and leaves the skin softer and brighter.
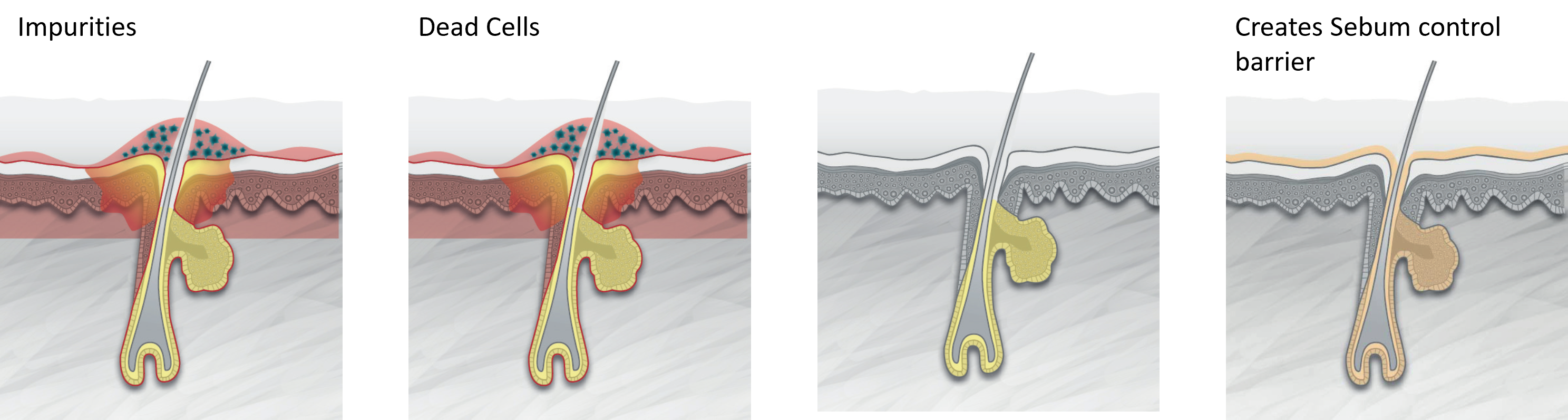
| Naturally, the desquamation of cells on the surface of the epidermis must be compensated by the keratinocyte renewal in the basal germinal layer. As these ascend to the upper layers, they begin the differentiation processes. This facilitates the construction of the protective horny layer, fulfilling its role as a skin barrier. The corneocyte elimination from the surface of the epidermis takes place partially under the influence of the environment (friction, chemical attacks, humidity, etc.). This desquamation process is intrinsically programmed and regulated by genes. The gradual degradation of intercellular junctions is influenced by proteases (enzymes that degrade proteins). The movements of these enzymes within extracellular spaces depend on the degree of lipid organisation and the stratum corneum hydration. This degradation is also linked, in part, to the composition and quality of the intercellular lipid substance. Protease activity not only promotes the desquamation process – it is also essential in maintaining the water content of the stratum corneum. This is because filaggrin, a protein produced through epidermal differentiation, directly induces the appearance of a ‘natural humidification factor’ in the upper layers of the epidermis. Thanks to a constant supply of epidermal cells that compensates for the loss of corneocytes on the skin’s surface, the stratum corneum maintains its constant thickness. As a result, the mechanisms of desquamation and proliferation are closely linked within the epidermis. |
THE BENEFITS OF EXFOLIATION
- Immediate elimination of dead cells from the horny layer: reduction in the horny layer thickness for maximum mechanical and biochemical protection
- Stimulation of cell renewal for a revitalising and toning effect on the skin
- Brightening action on skin pigmentation and radiance of the complexion, with a ‘glowing’ effect
- Maintenance of hydration in the outer layers of the epidermis
- Stimulation of the glycosaminoglycan synthesis
- Soothing of the skin’s texture and improved base for makeup
- Whether you chose a scrub or a peel, carrying out regular epidermal exfoliation can be very beneficial for the skin
- The effects are quickly visible – boosting the facial complexion’s luminosity and the appearance of skin texture – with significant benefits in the skin aging treatment.
⇒ All these benefits play a fundamental role in any regular skincare routine.

HOW DO YOU USE A FACIAL SCRUB CORRECTLY?
A scrub should be applied and performed on cleansed skin. Then, you should exfoliate the décolleté, neck and face, remembering to avoid the eye area.
We recommend scrubbing the epidermis without irritating it, by taking the time to exfoliate each area with soft and flexible movements.
To finish, rinse the scrub off with tepid water, and dry with a towel or tissue. Ideally, this should be followed by the application of a mask. This way, with the skin free of all impurities, it will be perfectly prepared to receive the specific active ingredients of a mask. Leaving the product on for fifteen to twenty minutes will allow the skin to enjoy the full effects of active ingredients.
CAN I USE TWO FACIAL SCRUBS AT THE SAME TIME?
Yes, this is an option for a combination skin type with shiny (oily) T-zone, and dehydrated -dry skin on the cheeks. To do this, simply apply a gentle scrub to more delicate areas and a purifying scrub to areas where enlarged pores are clogged with impurities.
HOW OFTEN SHOULD I SCRUB MY FACE?
For a perfect balance and respect for the skin, we recommend exfoliating once or twice a week, depending on the skin’s needs.
IS EXFOLIATION GOOD FOR DRY SKIN?
Dry skin suffers from a disorganisation of structural lipids. As a result, its cell renewal is slowed and the stratum corneum thickens. The skin may become dull and lose its shine. An adapted scrub will eliminate dead cells and stimulate natural cell renewal. As a result, the stratum corneum regains its functional role of protection. Your skin will look more supple and bright.
DOES THE SCRUB REMOVE THE TAN?
Melanin is mainly located from the germinative basal layer to the granular layer and very little in the stratum corneum. It is therefore physiologically impossible for mechanical or chemical exfoliation to remove the tan. On the t contrary, by exfoliating dead cells, the scrub helps to fight dull complexion, makes skin glow and also makes tan last longer!
DOES EXFOLIATED SKIN AGE FASTER?
By eliminating dead cells, exfoliation stimulates skin cell renewal, therefore supporting its restructuring. Contrary to popular belief, regular exfoliation does not tire the skin, nor does it accelerate aging. Instead, it promotes better cellular oxygenation and tissue regeneration, thereby optimising the penetration of active ingredients contained in creams and serums. However, make sure to keep to a frequency of once or twice a week at maximum.
OILY SKIN, SHOULD IT BE EXFOLIATED?
Oily skin should be exfoliated once or twice a week, like other skin types. Beyond that, scrubbing will stimulate the sebum secretion – already excessive in oily skin. Too frequent exfoliation will serve only to maintain an overproduction of sebum. A vicious circle would be established.
CAN YOU USE ONE SCRUB FOR FACE AND BODY?
It is not recommended to use the same product for the face and for the body. The skin structure, thickness, sensitivity and hydrolipidic film are very different on the body. Scrubs should therefore be suited to the specificities of the face and body, depending on the area to be exfoliated.
MORNING OR EVENING: WHEN IS BEST TO SCRUB?
It’s better to exfoliate in the evening, rather than in the morning. This is because, at night, the skin will be more receptive to the cell renewal stimulation induced by exfoliation. At night, exfoliated skin is less exposed to stress and can regenerate more easily.
SUMMING UP:
- Whether it’s a serum or a protective cream, any skincare will increase its effectiveness if applied to perfectly cleansed and regularly exfoliated skin. That’s why it’s important to underline the significance of these fundamental actions for the restoration or maintenance of healthy, resistant and beautiful skin.
Go to Être Belle Scrubs and Exfoliators Category {link}